Kishi matrix grain size effect and fracture bmamor on bending strength and fracture toughness in multi toughened al2o3 proceedings of the 16th annual conference on composites and advanced ceramic materials.
Ceramic grain size fracture toughness.
Unlike fracture toughness the notch fracture toughness of a ceramic is not a constant.
A review of the fracture energy and toughness data for dense ceramics at 22 c shows maxima commonly occurring as a function of grain size.
Rather it increases with the notch root radius ρ in a notched specimen.
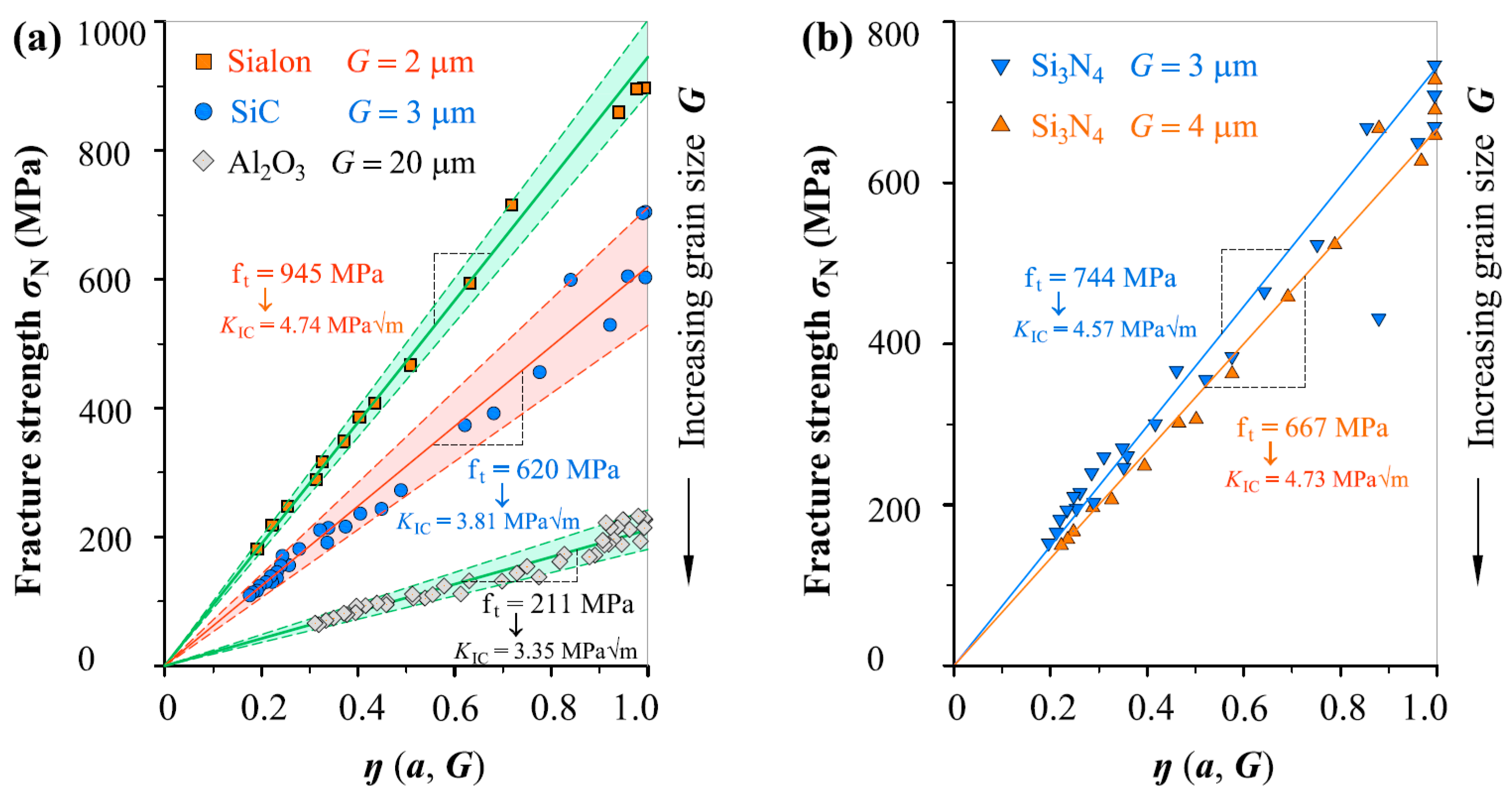
Three point bending fracture toughness and static fatigue crack growth tests of alumina specimens with various grain sizes were carried out to investigate the effects of grain size on bending strength fracture toughness and static fatigue crack growth rate.
Above this grain size a spontaneous transformation from tetragonal to monoclinic phase occurred.
Vickers indentation and single edge v notched beam sevnb techniques have been used to measure hardness and fracture toughness respectively.
The fracture toughness was almost constant for ceramics with the grain size up to 0 40 µm and then grew with increasing grain size up to 7 8 mpam 0 5 for ceramics with grain size of 1 8 µm.
Certainly this is only the necessary condition for obtaining tough ceramic graphene composites which does not.
Such maxima are most pronounced for non cubic materials where they are often associated with microcracking and r curve effects especially in oxides but often also occur at too fine a grain size for association with microcracking.
Ceramic engineering and science proceedings undefined 164 171 2008.
In this study by analyzing the fracture measurements of eight different notched ceramics with an average grain size g of 3 40 μm a simple model describing the relation between the notch fracture toughness and fracture toughness.
The fracture toughness was almost constant for ceramics with the grain size up to 0 40 μm and then grew with increasing grain size up to 7 8 mpam0 5 for ceramics with grain size of 1 8 μm.
The fracture toughness of zirconia alumina and silicon nitride ceramics zirconia and alumina single crystals silicon carbide as well as silicon nitride ceramic particulate composites silicon nitride laminated composites and other ceramics materials were studied by a single edge v notched beam sevnb method.
Room temperature fracture toughness and hardness of spark plasma sintered pure b 4 c ceramics with grain sizes ranging from 120 nm to 17 μm have been studied.
To achieve the fracture toughness of 4 3 mpa m 1 2 which implies 35 fracture toughness enhancement compared to pure alumina the gb length should exceed 1 4 μm which corresponds to the grain size exceeding to 2 7 μm.
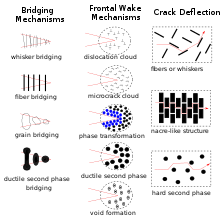
Cracks cannot easily propagate in tough materials making metals highly resistant to cracking under stress and gives their stress strain curve a large zone of plastic flow.